Basic notes on the Hebrew script
The Hebrew script has unique characteristics that distinguish it from other languages.
Special features
- The first Hebrew writing system is the same as the Phoenician writing system.
- The Aramaic or square alphabet is still in use today.
- It consists of 22 letters.
- This alphabet records only consonants.
- Vowels are represented by dots and dashes and in modern Hebrew these signs (niqqud) are rarely used, mainly in children's literature and poetry.
- Letters are not distinguished between upper and lower case, but between handwritten and typographic.
- Hebrew is written from right to left. This applies to both writing and reading.
The Hebrew Alphabet
Similar to the Greek "Alphabet" - from the first two letters Alpha and Beta - , the Hebrew "Alephbet" comes from Aleph and Bet.
Table of the Hebrew Alephbet with the first letter in the upper right corner.
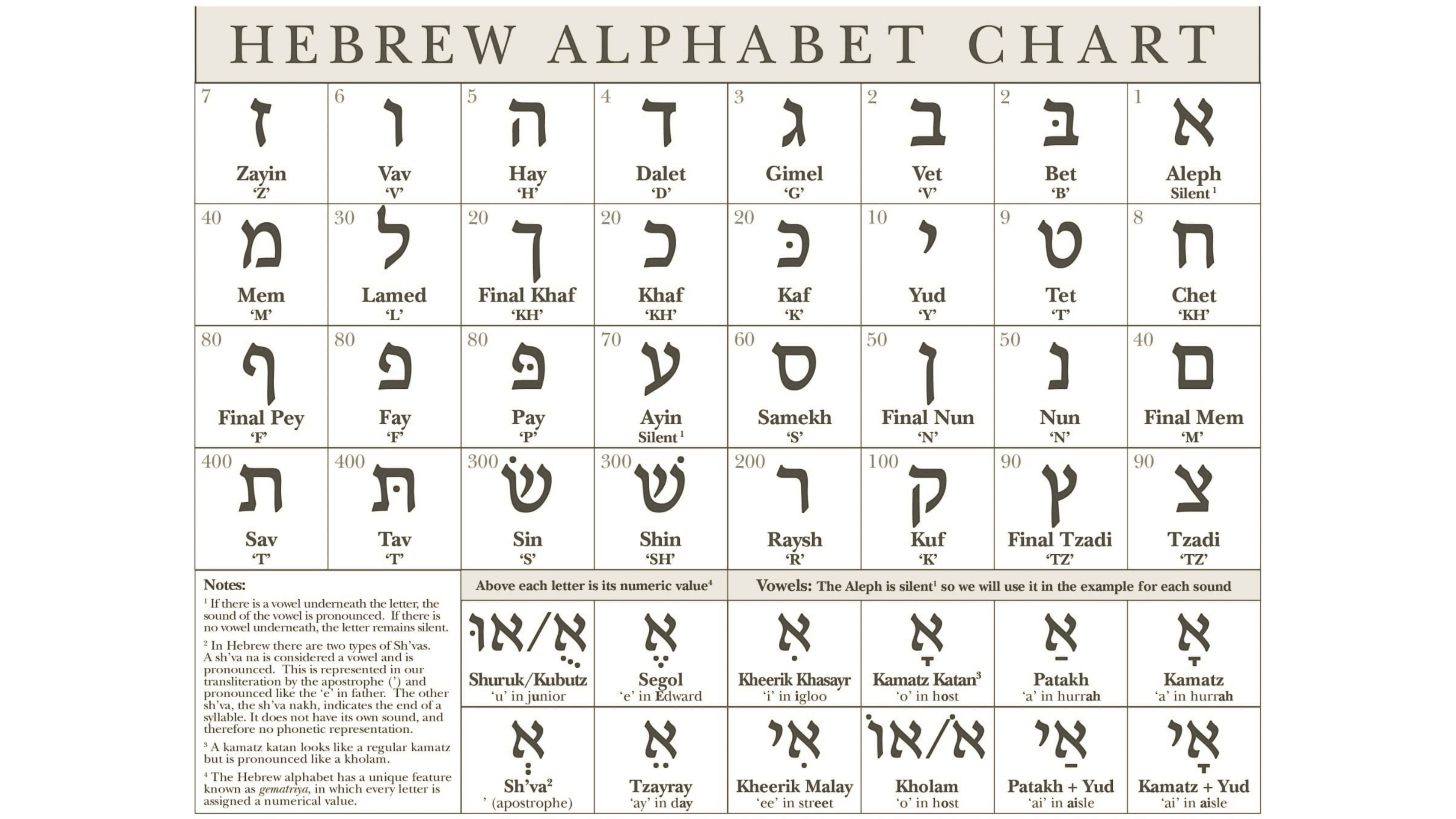
The Hebrew alphabet consists of 22 letters, all consonants.
Letters of Alephbet with many similarities
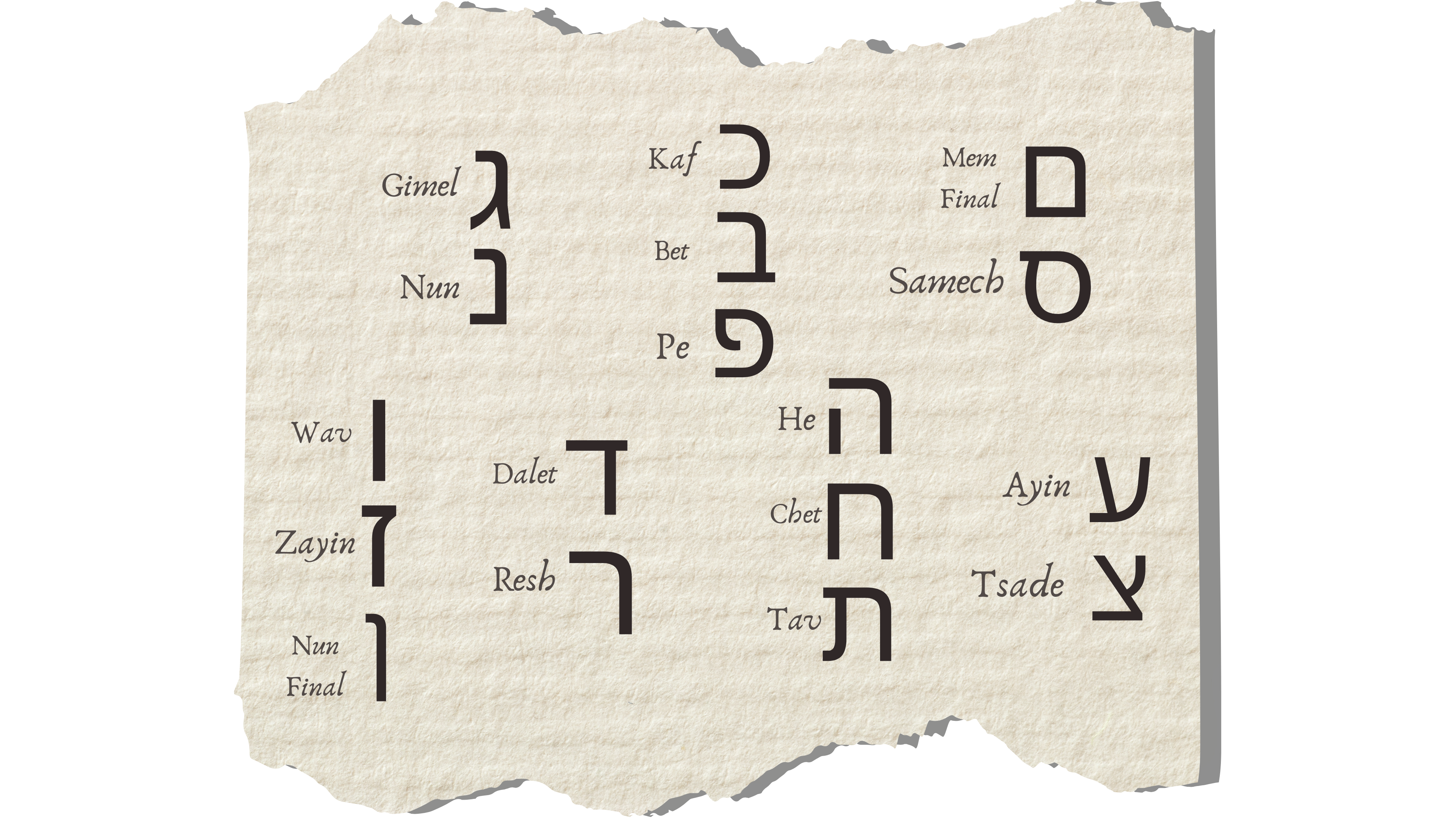
The five final letters: (ך, ם, ן, ף, ץ) have a different shape when they are at the end of the word.
Vowels & Marks (Nicud - נִקּוּד)
- Hebrew does not have vowels as separate letters.
- Vowels are marked with dots and dashes below or above the letters. These are mainly used in texts for beginners or religious texts.
- In everyday use, vowels are often omitted and are perceived in context.
- Aleph is not a vowel. א is considered a consonant and corresponds to the small (᾿).
Letter ConnectionClick to apply
- Unlike Arabic, the Hebrew letters are not joined together.
- Each letter is written separately.
Special Cases
Distinction B/V, P/F:
ב (Bet) has a B sound when it has a dot (בּ) and a V sound when it does not.
פ (Pe) has a P sound with a dot (פּ) and F without a dot.
Use ו (Vav) as a semitone:
It can be read as V, but also as U or O when it has a special sign on it.
Writing numbers:
Numbers in Hebrew can be written also with letters of the alphabet, e.g. א (1), ב (2), ג (3).
Calligraphy:
There are different styles of writing, such as the standard printed form and the handwritten form (Rashi, Stam).
Differences between Greek and Hebrew alphabet
| GREEK ALPHABET | HEBREW ALPHABETHebrew alphabet |
|---|---|
| Greek is read and written from left to right. | Hebrew is read and written from right to left. And reading a book in Hebrew starts from the last page of the book, as it is understood in Western typography. |
| There are 24 letters in the Greek alphabet: some are vowels (a, e, i, h, y, o, o), and some are consonants (b, c, d, z, etc.) | There are 22 letters in the Hebrew alphabet and they are all consonants. The vowels are dots and dashes added below, next to or above the consonants. |
| Letters in Greek can be uppercase or lowercase. | The letters in Hebrew have only one form. |
| The last letters of a word in Greek remain the same except for the final sigma (ς). | Five Hebrew letters have different forms when they appear at the end of a word. |
| Ancient Greek is pronounced differently depending on the way it is pronounced. For example, there is the so-called herasmic pronunciation which pronounces all vowels and does not pronounce most diphthongs monophonically. In Greece, we pronounce ancient Greek as we read Modern Greek (Rohlichlinian accent). | Hebrew is pronounced in different ways today. The Sephardic or Middle Eastern pronunciation is used in Israel and is the new Hebrew language. |
Writing Exercise
To practice, try writing the following:
שלום (Shalom) - Means "Peace" or "Hello".
- תורה(Torah) - The Torah, the sacred scripture of Judaism.
- חיים (Chayim) – Life.
- אהבה (Ahavah) – Love.